Sturgeon Caviar ageing/maturation
What is Sturgeon Caviar?
-
Sturgeon Caviar is the product made from fish eggs of the Acipenseriae family by treating with food grade salt.

-
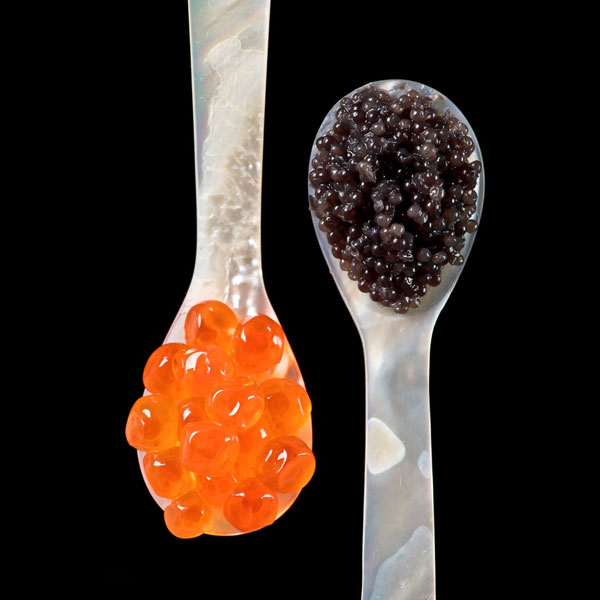
Salmon roe (left) and sturgeon caviar (right) served with mother of pearl caviar spoons to avoid tainting the taste of the caviar.
-
-
Sturgeon Caviar is a delicacy consisting of salt-cured roe of the Acipenseridae family. The roe can be "fresh" (non-pasteurized) or pasteurized, with pasteurization reducing its culinary and economic value. Traditionally, the term caviar refers only to roe from wild sturgeon in the Caspian Sea and Black Sea (Beluga, Ossetra and Sevruga caviars). Caviar is considered a delicacy and is eaten as a garnish or a spread.
-
The rarest and most expensive form of caviar comes from the critically endangered beluga sturgeon that swims in the Caspian Sea

-
Black Beluga caviar

-
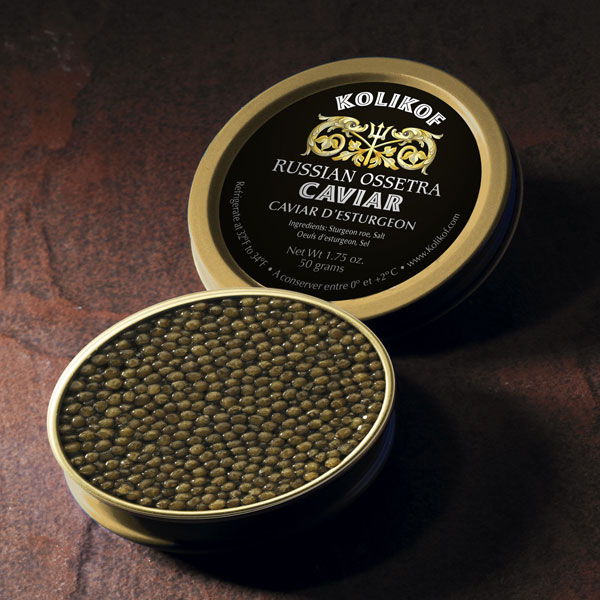
Russian Ossetra sturgeon

-
Russian Ossetra sturgeon caviar


-
Sevruga sturgeon

-
Sevruga sturgeon caviar

How to process aging/maturation and preserve Sturgeon Caviar in chilling conditions?
-
Sturgeon caviar is often packaged into 2-part metal tins of 1.8kilos (4 lb.) that have a slot for drainage along one side wall. Lids are placed onto containers that have been overfilled by 10-15% and pressed down. The tins are laid on their sides to allow fluid to drain from the product during curing. After 2 hours, the tins are placed under weight to further compress the caviar and remove excess liquid and air. Finally, a thick rubber bank is placed around the circumference of the tin to secure the lid. Product is aged for a number of months at super chilled conditions of -2℃/28.40℉ to 8℃/46.40℉. For retail sales, the caviar is repackaged into small containers generally glass jars (1,2, and 4 oz.) with screw cap, crimp seal, or press-on vacuum closures. Tetail tins up to 100g and wholesale tins of up to 1 kg are also sold. Caviar is also packaged in crystal and in gold plated containers.
-
(Source:
-
Handbook of Food Science, Technology, and Engineering, Volume 4, edited by Yiu H. Hui; Caviar and fish roe, 161- 17, Gleyn Bledsoe and Barbra Rasco)
-
-
-
When the original tins of caviar (500g, 1kg or 1.8 kg) arrive, caviars are stored in cold rooms for maturation. A long process of ageing begins. The salt will be absorbed by osmosis: this fusion is what will give the caviar grains their texture, taste and uniqueness. A too young caviar is tasteless and it is necessary to wait at least 3 months after the harvest for the caviar to reveal its best aromas. Like a wine cellar master or a cheese affineur, caviar expert, monitors the good process of caviar aging until they have reached full maturity.
-
(Source:
-
Kaviari expertise - Caviar ageing / maturation
-
-
-
Most dealers say that surgeon caviar needs to sit a few weeks to be at its best. As the eggs absorb the salt, the individual globules plump up, and the taste becomes stronger and more complex, like wine aging in oak.
-
Ideally, fresh caviar needs to be kept at twenty-six degrees Fahrenheit (26°F/-3.333°C) at all times. Because of the salt, the perishable roe will neither freeze nor spoil at that magic temperature. Should the thermometer drop just one degree (25°F = -3.889°C), however, the caviar will begin to freeze. When it comes time to thaw the fragile eggs, their casings will crack, turning the product into mush. Even when fresh caviar is stored at precisely twenty-six degrees (26°F/-3.333°C), it will remain at its peak for only six or eight months.
-
Preserving the tradition of making caviar - “the maturation is.” Must let caviar mature, two months to one year. The merchandise should be aged, controlled like salmon or vodka. The maturation is what makes caviar unique.” The French think of it as a delicacy.”
-
(Source:
-
CAVIAR - THE STRANGE HISTORY AND UNCERTAIN FUTURE OF THE WORLD'S MOST COVETED DELICACY, INGA SAFFRON)
-
-
-
Example flow chart for caviar processing
-
Maturing/Maturation: The process from salting until the fish is salt-matured.
-
Chilling: The process of cooling fish and shellfish to temperature approaching that of melting ice.
-
(Source:
-
Figure 19.1, Page 243, SECTION 19 – PROCESSING OF STURGEON CAVIAR, CODE OF PRACTICE FOR FISH AND FISHERY PRODUCTS, CAC/RCP 52-2003
-
-
19.18 Cooling and maturation (Processing Step 18)
-
Potential hazards: microbiological contamination
-
Potential defects: decomposition, quality deterioration
-
Technical guidance:
-
Packaged caviar should be stored in an appropriate manner prior to final cold storage (e.g. in a refrigerator at a temperature between 2 °C and 4 °C for 24 hours) upon packaging to facilitate salt absorption, equilibrium and maturation (equal salt distribution in caviar, giving enough time for saltwater removal) and to minimize microbial growth.
-
Laboratory checks should be performed for proper caviar salt content (e.g. by water phase salt determination or by water activity measurement and weight as appropriate) after maturation is complete.
-
The cooling system should be cleaned and equipped with a thermometer and thermograph to frequently monitor and record caviar temperature.
-
The cooling system should be frequently calibrated to ensure accuracy and efficiency.
-
-
-
19.21: Cold storage (Processing Step 21)
-
Potential hazards: microbiological contamination
-
Potential defects: freezing, decomposition and quality deterioration
-
Technical guidance:
-
The product should be held at cold storage temperatures between -4℃/24.80℉ and 0℃/32.00℉. Care should be taken to avoid temperatures below -5℃/23.00℉, which will cause freezing and quality deterioration. Normally freezing or frozen storage are not permitted, unless it can be demonstrated that quality deterioration is avoided.
-
The caviar cold storage room should be cleaned and disinfected based on a continuous cleaning and disinfection schedule.
-
The chilled storage facility should have a temperature-monitoring device and preferably a continuous recording unit to monitor and record ambient temperatures properly.
-
The temperature-monitoring system should be equipped with an alarm to alert of any fluctuations outside of the permitted range.
-
All time/temperature monitoring and record systems should be calibrated regularly through a permanent schedule to ensure accurate and precise performance.
-
Containers of caviar should be periodically checked for loss of vacuum or can corrosion; any affected containers should be rejected.
-
(Source:
-
Page 252, 254, SECTION 19 – PROCESSING OF STURGEON CAVIAR, CODE OF PRACTICE FOR FISH AND FISHERY PRODUCTS, CAC/RCP 52-2003
-
)
-
-
-
-
Sturgeon Caviar must be stored at about 26°F/-3.333°C to 28°F/-2.222°C to keep it fresh and tasty for an extended period of time.
-
Sturgeon Caviar is very sensitive to temperature fluctuation as well as extended exposure to air.
King Son Convertible IFP Aging Chiller, the solution to process aging/maturation and preserve Sturgeon Caviar in chilling conditions
-
IFP Chilling is the temperature range, defined between 0°C/32°F and above Initial Freezing Point (IFP) of food.
-
IFP Chilling temperature can be used to process and preserve fresh fruits, vegetables, meat and fish at a little below 0°C/32°F - but above the initial freezing point of food – without freezing/icing, gives food maximum shelf life.
-
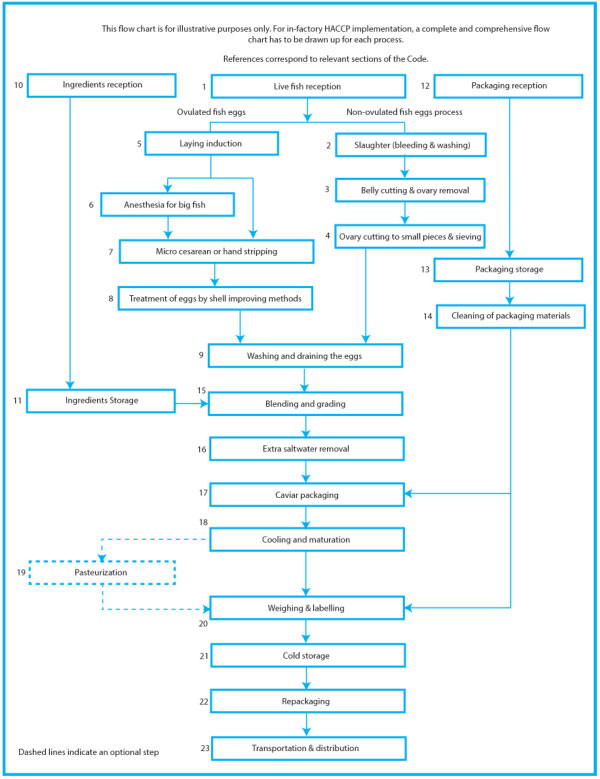
King Son Constancy IFP Chilling Technology commercializes the economic value of the temperature ranges between 0°C/32°F and above Initial Freezing Point (IFP) of food, without freezing/icing, that performs temperature fluctuation ± 0.3°C/0.54°F and humidity fluctuation ± 5 % for food preservation in food industry.
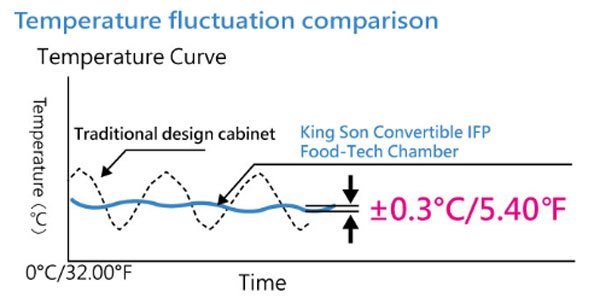
-
The effects of King Son Constancy IFP Chilling Technology applied on the fresh food preservation mainly includes
-
King Son Constancy IFP Chilling can inhibit respiration, delay the respiratory peak and reduce the loss of nutrients. The exhaled volume of CO2 in the King Son Constancy IFP Chilling is less than that stored in normal temperature.
-
King Son Constancy IFP Chilling won’t destroy the cells, but improve the quality of fruits, vegetables and meats in the vicinity of freezing temperature. In order to prevent from forming ice, fruits will secrete large amounts of antifreeze (its main ingredients are glucose, amino acids, aspartic acid etc.) to reduce the freezing point, or decompose the starch into sugar. These physiological changes improve the quality of fruits and vegetables in different degrees.
-
King Son Constancy IFP Chilling can inhibit the growth of microbial efficiently. Under the condition of King Son Constancy IFP Chilling, water molecules in fruits or vegetables are arranged in an orderly state, which reduce the content of free water available for the microbial. In the short and mid period preservation, King Son Constancy IFP Chilling can inhibit multiplication of microorganisms, better than the frozen temperature.
-
Since King Son Constancy IFP Chilling can inhibit chemical reaction strongly, the food quality in King Son Constancy IFP Chilling is better than that of the normal cold storage. King Son Constancy IFP Chilling also can inhibit lipid oxidation, non-enzymatic and other chemical reaction. The key for King Son Constancy IFP Chilling preservation is to realize a hibernation state of the product. The “hibernation” process is a cooling process during which the product can reduce its activity ability and energy consumption through the self-adaption, starting from the change of components within cells, and at the same time ensuring their own living life characteristics. It is a typical phenomenon of natural adaption.
-
-
King Son Constancy IFP Chilling Technology application process
-
Keep Freshness
-
Preservation
-
Aging
-
Fermentation
-
Rigor off
-
Dehydration
-
Inspissation
-
-
King Son Convertible IFP Aging Chiller is a new refrigeration and food preservation solution for the modern AIoT-era. It is incorporated with A7 Intelligent Food-Tech Controller and designed with Constant Temperature and Humidity Multiple Points Monitoring and Servo Control Technology to perform Convertible Temperature Refrigeration System between precision refrigeration and precision freezing for 5 novel next generation refrigeration technologies.
-
King Son Constancy Precision Refrigeration Technology (0°C/ 32.00°F - 6°C/ 42.80°F)
-
King Son Constancy IFP Chilling Technology (0°C/32.00°F– above Initial Freezing Point of food)
-
King Son Constancy Superchilling Technology (- 1.5°C/29.30°F to -2°C/28.40°F, just below Initial Freezing Point of food)
-
King Son Constancy IFP Superchilling Thawing/Tempering Technology (2°C/28.40°F to -5°C/23.00°F)
-
King Son Constancy Precision Freezing Technology (- 12°C/10.40°F)
-
that preserves and processes food in uniform conditions and environments, with temperature fluctuations ± 0.3°C/ 0.54°F and humidity fluctuations ±5%. King Son Convertible IFP Aging Chiller is an AIoT machine which incorporates King Son Real-Time Cloud-Based AIoT Operation Tracking and Monitoring APP System and Platform for remote distance servicing and collaboration – thus helping build new partnership opportunities through AIoT eco-system.
-
King Son Convertible IFP Aging Chiller
-
King Son Convertible IFP Aging Chiller is designed with King Son Constancy IFP Chilling Technology mainly, specifically designated applied for high value fruit, vegetable, fish, meat process and preservation between 0°C/32°F and above Initial Freezing Point of food, without freezing/icing.
-
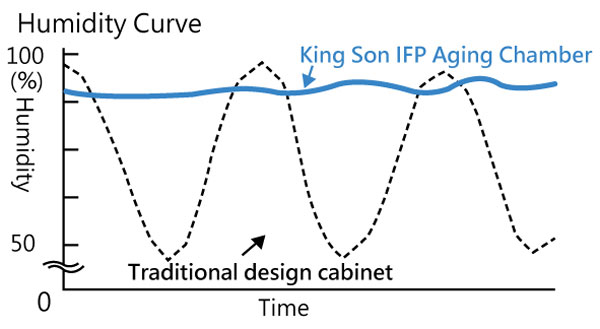
The blue color temperature graphics of actual lab experimental testing results demonstrated the return temperature after defrosting is still above the set freezing point of food -0.5℃/31.10℉, no freezing/icing condensed on food.
-
-
King Son Convertible IFP Aging Chiller ages food above its initial freezing point (IFP) thereby contributing to food’s maturation, firmness, persistence, and flavor, as well as preserving food either above IFP or in super-chilling temperature to extend longer shelf life or distant delivery, when necessary.
-
The aim of superchilling is to preserve food products at temperatures just below their initial freezing point, with a light, thin layer freezing ice on the surface of the food, which is low enough to substantially reduce bacterial activity but high enough to avoid significant levels of bigger size ice crystal growth as frozen does that can cause food structural damage. Traditional frozen meat can be extended for a long time. However, large amounts of water frozen out lead to serious texture microstructural change and drip loss after thawing.
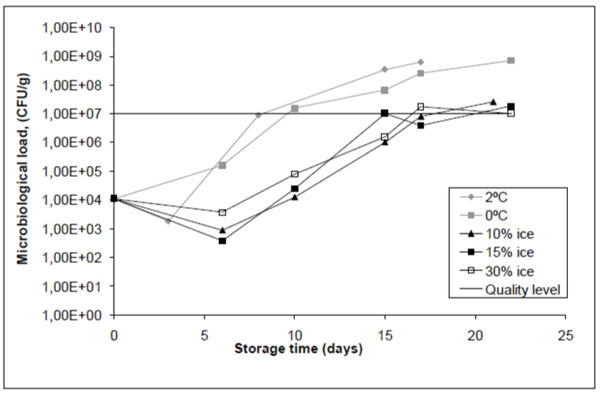
-
The quality limit of 107 CFU/g represents a usual microbiological quality measure, above which food is regarded as unfit for human consumption.
-
Figure 4 Microbiological load (total count) for unpacked chilled and superchilled salmon fillets
-
(Source:
-
Stevik, A.M. 2007. Microbiological level of unpacked, chilled and superchilled salmon fillets. In SINTEF Energy Research, Trondheim
-